Search

News & Events
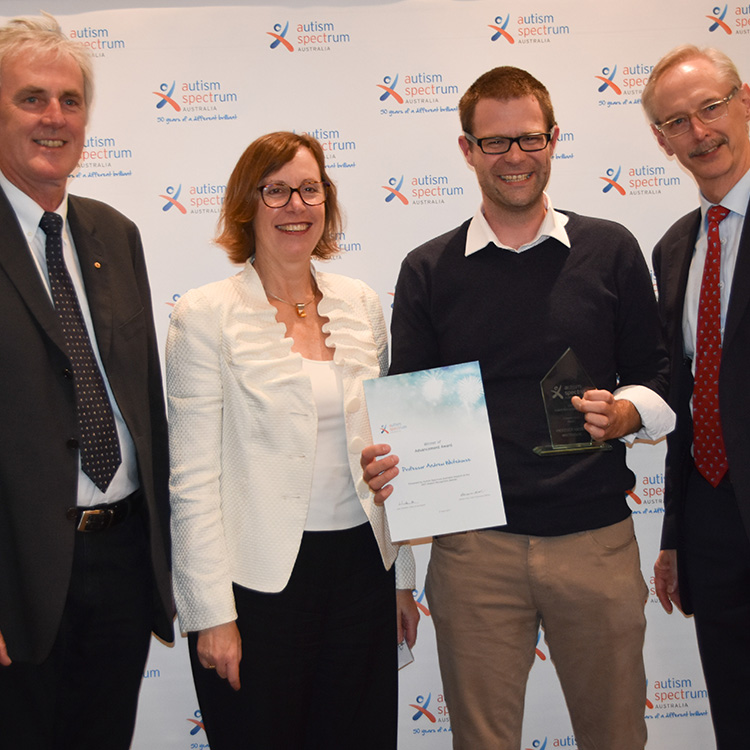
Autism researcher wins accolade for science videosProfessor Andrew Whitehouse has been awarded an Autism Spectrum Australia Recognition Award for his work communicating scientific findings to families.

News & Events
Event: An Evening With Cystic Fibrosis ScientistsJoin us for an annual research update from WA cystic fibrosis researchers.Find out the latest research findings in Cystic Fibrosis.

News & Events
8 tips to raise happy kidsAll parents want their children to be happy. But in our rapidly changing modern world what does that actually mean? Prof. Stephen Zubrick provides his top tips.
News & Events
1 in 3 young people in detention has alcohol related brain damageAbout a third of young people in youth detention in Western Australia have Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD), data has found.

News & Events
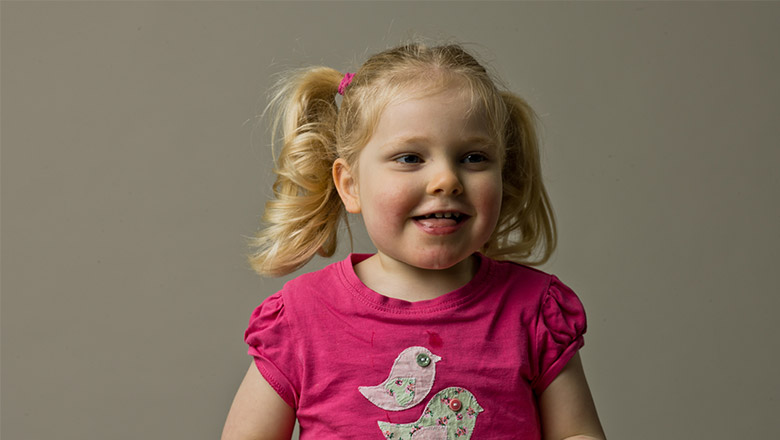
Video: One brave little girl's battle with Rett syndromeImagine your baby is developing normally, then suddenly she starts losing skills. Watch Marlee's story below and find out what researchers are doing.

News & Events
Video: Why you're wasting your money on bottled waterThe Kids Research Institute Australia nutritionist Dr Roslyn Giglia says Australians are spending over $500 million a year on bottled water, when tap water is healthier.

News & Events
The Kids Research Institute Australia researchers finalists for 2016 Eureka PrizesThree Perth researchers from The Kids Research Institute Australia have today been named finalists for the 2016 Australian Museum Eureka Prizes.

News & Events
Survey finds parents don’t always know if their kids are struggling emotionallyAs a parent of two teenage daughters, I like to think I know what's going on in their lives and how they are feeling.
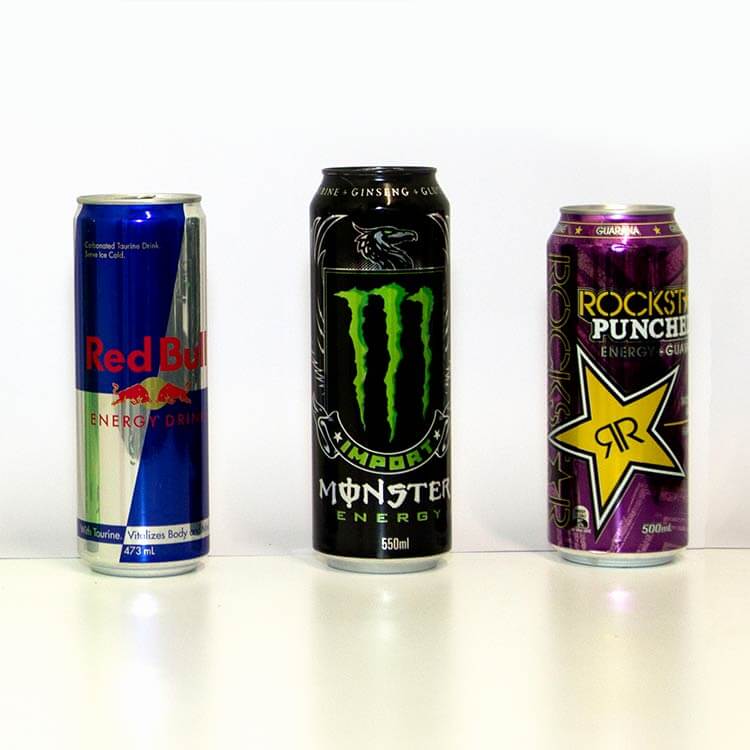

News & Events
Australian first study looks at energy drink harm in young peopleResearchers at the Telethon Kids Institute will study the health impacts of energy drinks on young people and develop guidelines for reducing consumption.

News & Events
Australian Early Development Census National ConferenceThe Australian Early Development Census National Conference 2015 will be held from 18-20 February 2015.
