Search

Frangipani Family Day is a free community event for young neurodiverse children and their families in WA.

CliniKids has partnered with Autism CRC to deliver an online self-paced short course which explores the Recommendations included within the National Guideline for supporting the learning, participation, and wellbeing of autistic children and their families in Australia.
There is lots of news to report from the clinic including holiday shutdown dates, appointment scheduling, staff updates, changes to creche, and service availability.

The Kids Research Institute Australia’s CliniKids is excited to introduce an online autism seminar series in 2024, designed to inform families, clinicians and educators about the latest autism topics and research.

For Occupational Therapy Week, we asked our OTs to share their favourite resource and how they like to use it.

We are currently working through several clinical audits to ensure that we are meeting our service delivery standards and governance requirements. As part of this, we have audited our Service Agreements to ensure that we have a signed agreement on file for all our clients. This agreement is an NDIS
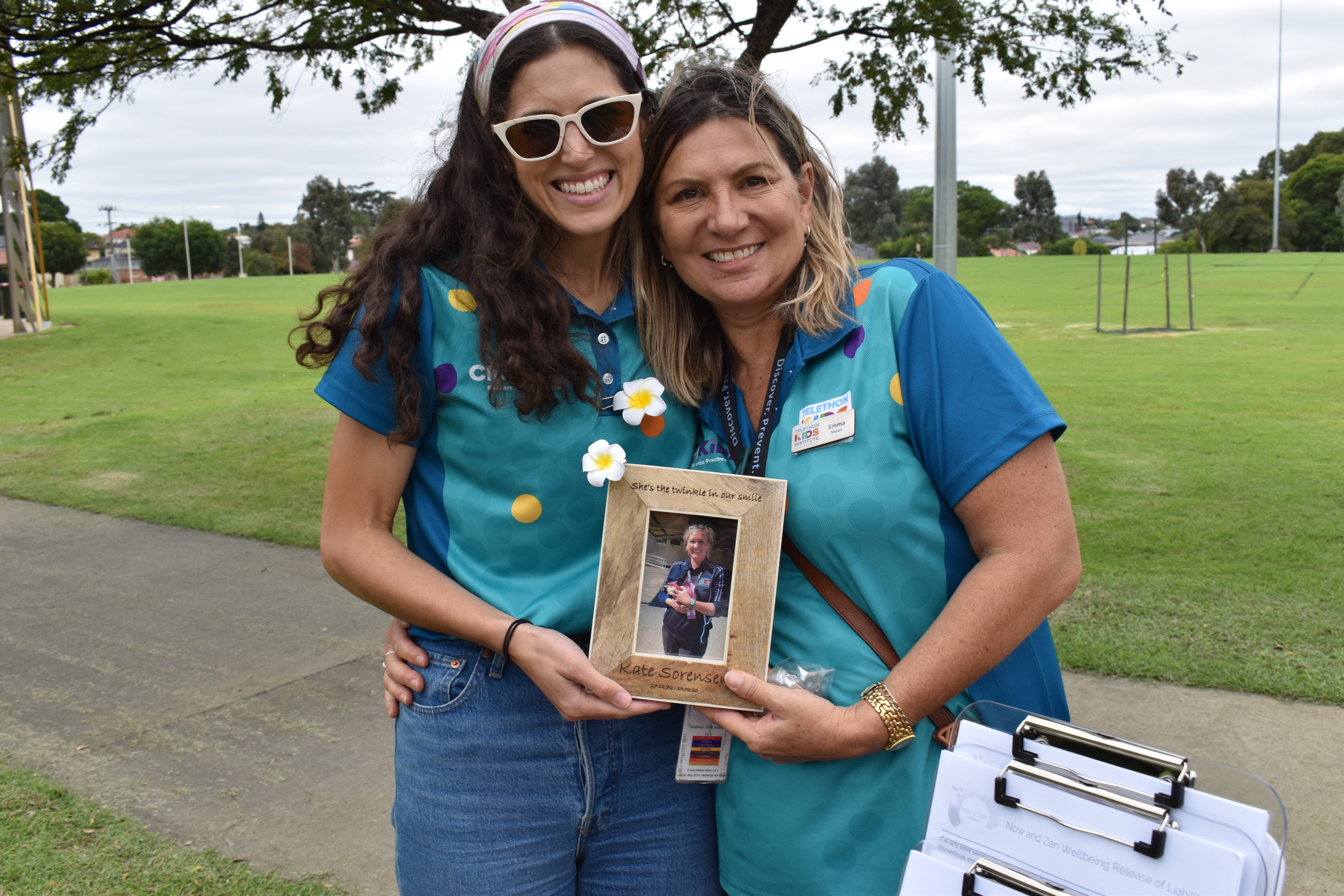

CliniKids held Frangipani Family Day recently – an event organised to honour the wonderful contribution of its much loved and dearly missed colleague, the late Kate Sorensen.

CliniKids is committed to involving consumers and the community in all aspects of our research and service delivery. One way we do this is by providing the opportunity for consumers and community members to contribute through our community reference groups.
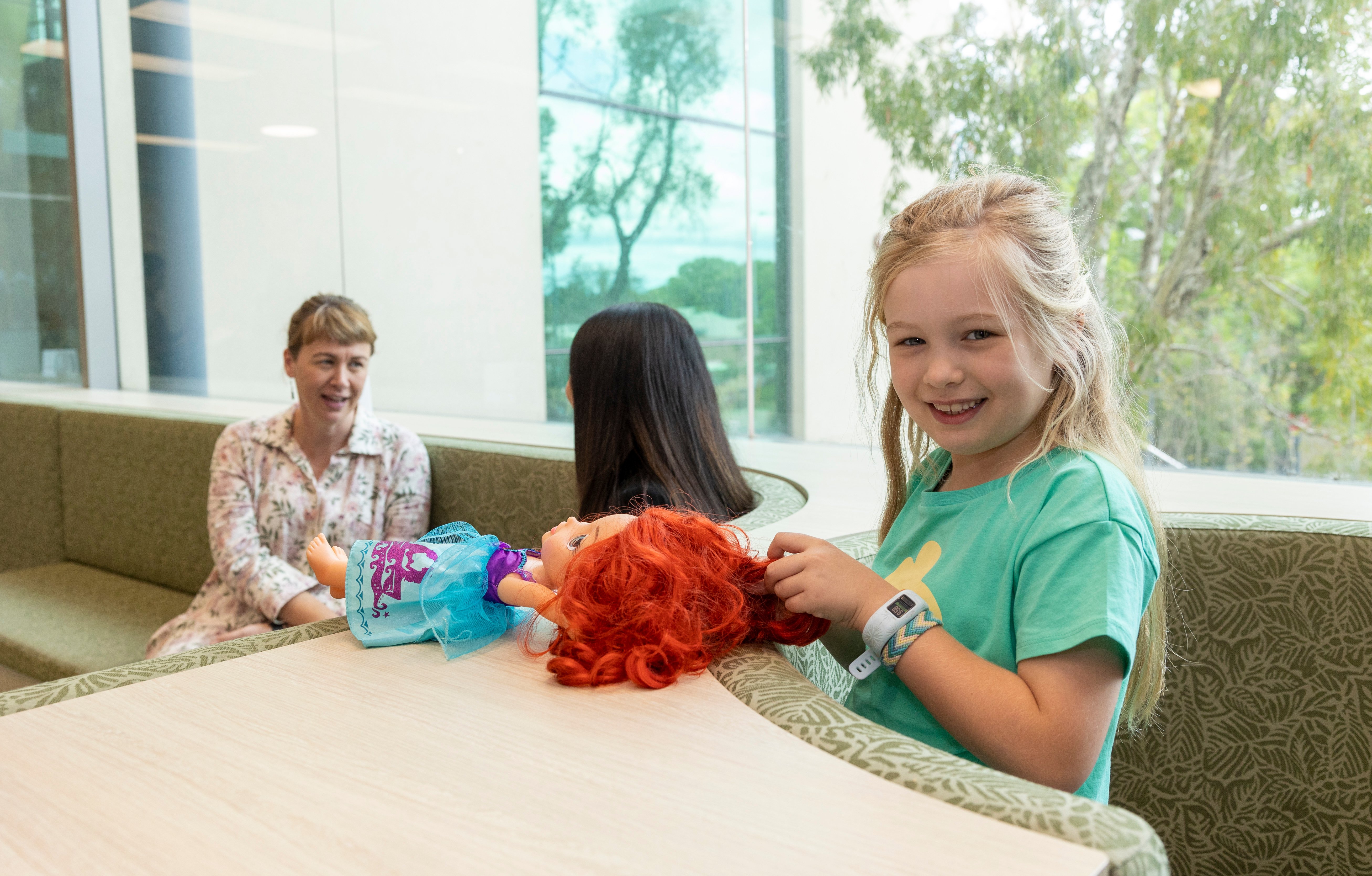
Frangipani Family Day is an opportunity for CliniKids to celebrate the families we engage with through our clinical services and research.

We are aware that many of our clients are either starting kindy or are transitioning from kindy to fulltime school and may require a different day/time for their regular therapy sessions at CliniKids.
