Search

News & Events
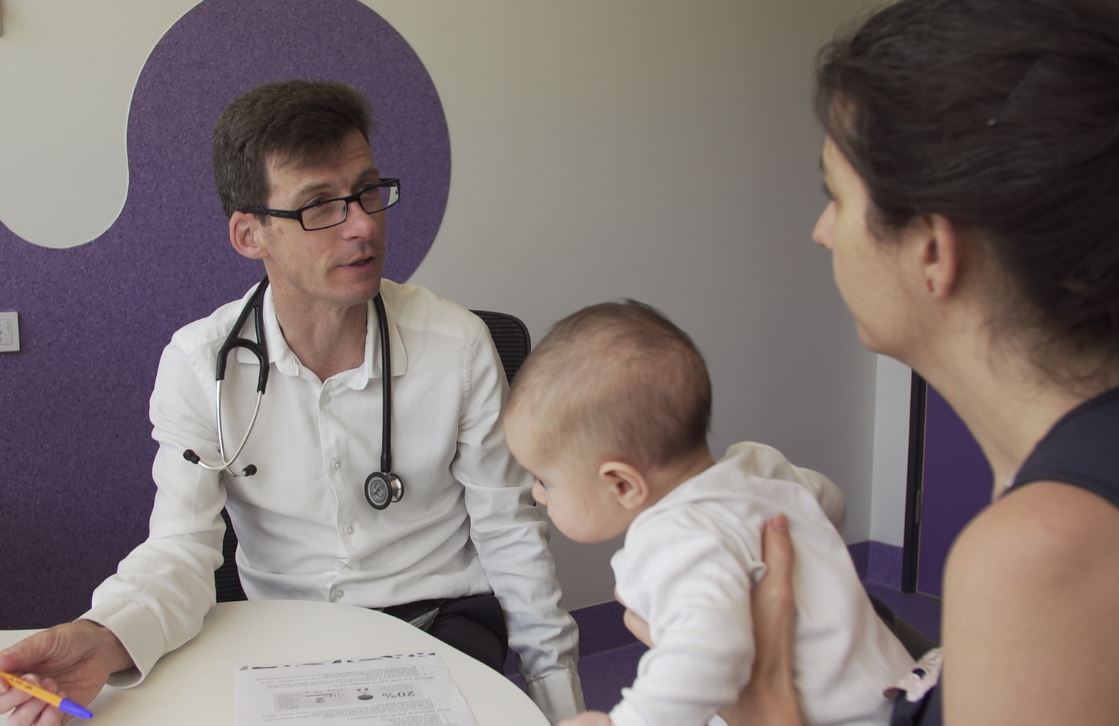
New research prepares for COVID-19 vaccine roll-outAs the world waits for a COVID-19 vaccine Perth researchers are getting one step ahead – embarking on a new study designed to prepare parents and government for a potential Australia-wide vaccination program.
News & Events
Perth’s Aboriginal babies show first signs of ear disease at just eight weeksThe Kids Research Institute Australia researchers have found close to 40 per cent of Aboriginal babies begin to develop middle ear infections between two and four months of age in a first of its kind study in metropolitan Perth.

News & Events
Kids hip hop to stop painful skin infections in the Kimberley regionThe Kids Research Institute Australia researchers have launched the Hip Hop 2 SToP video featuring school kids participating in their SToP Trial project designed to see, treat and prevent skin infections in WA’s Kimberley region.

News & Events
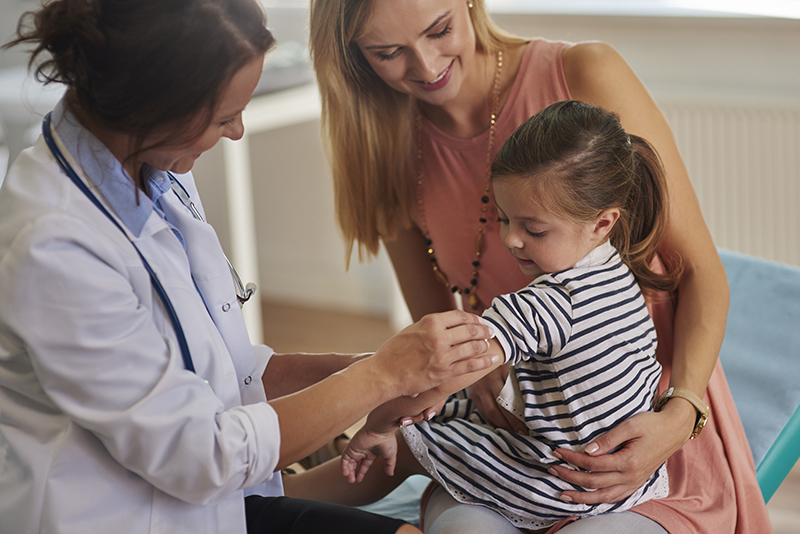
Important things you should know about this year’s flu seasonNews headlines about the large number of life-threatening cases of the flu in Western Australia this winter have been hard to miss - find out what you can do to protect your family.

News & Events
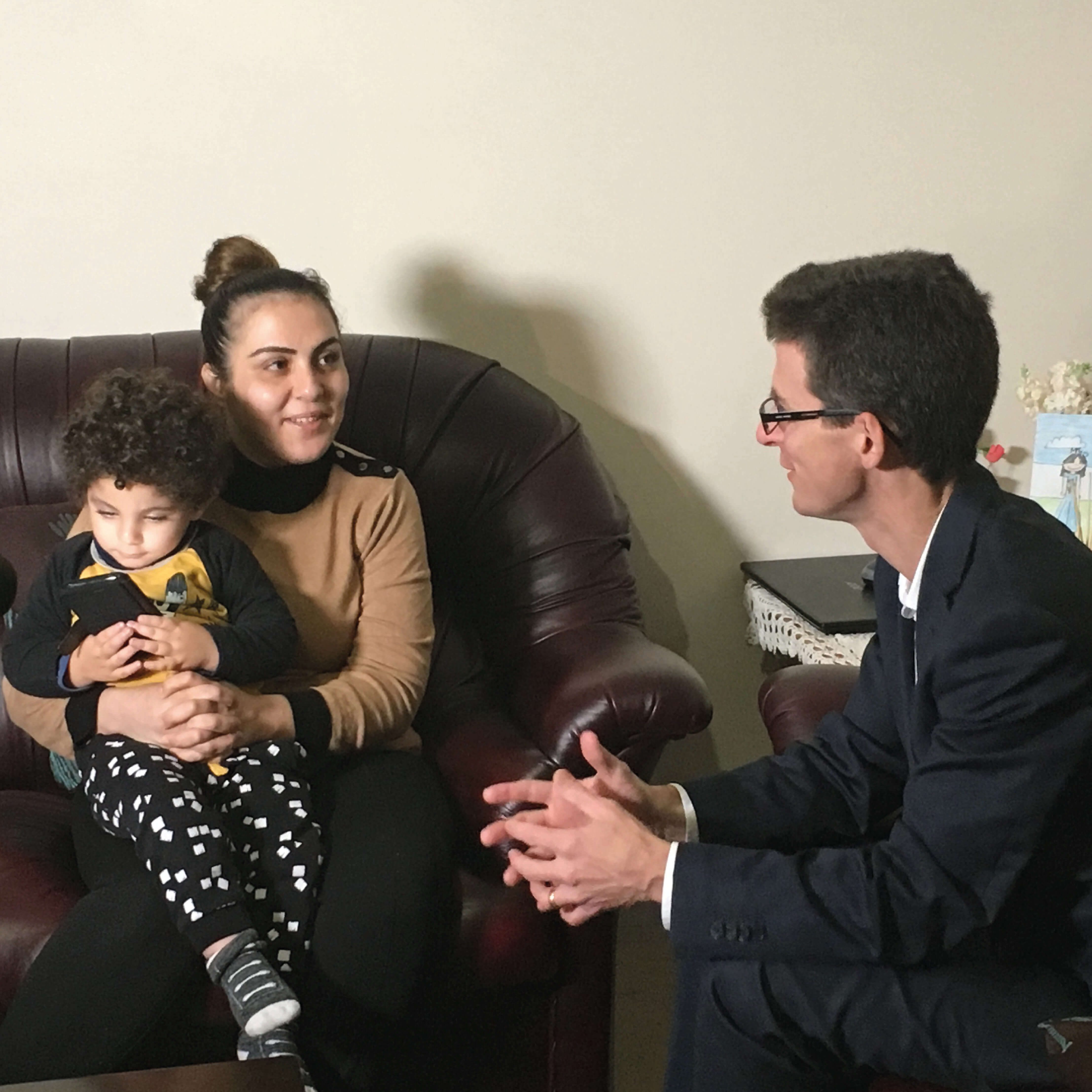
WA parents oblivious to true danger of the fluPerth parents are underestimating the serious consequences of the flu, with only 19 per cent of children under five years of age currently immunized against the virus ahead of the peak winter flu season.
Learn more about the Wesfarmers Centre of Vaccines and Infectious Diseases
To improve the health of the community through immunisation and prevention of infectious diseases, we are conducting clinical trials of vaccines.

The CHIP Study investigates how burn injuries in children affect their immune system.
Allergies have been on the rise in Australia over the past 20 years, with three out of every 10 babies born each year now developing a food-related
The year 2020 has been marked by possibly the greatest health challenge to face modern society. The emergence of COVID-19 as a novel human pathogen
