Search

News & Events
Researchers receive crucial near miss fundingCongratulations to three outstanding The Kids Research Institute Australia researchers who have received second chance WA health funding designed to support researchers who have narrowly missed out on highly competitive national funding.

News & Events
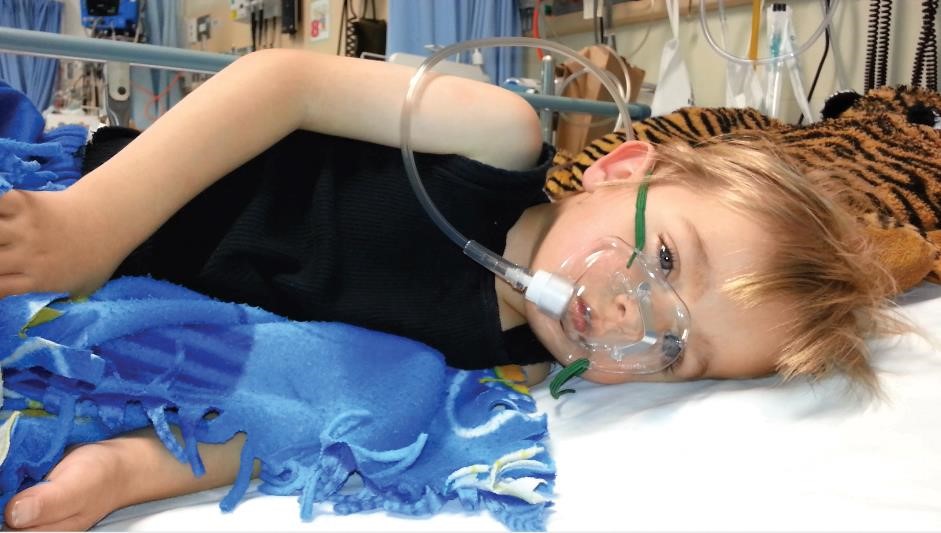
Study finds high rates of chronic lung disease in remote-living Aboriginal childrenAlmost one in five children across four remote Kimberley communities has some form of chronic lung disease, according to a new study co-designed and conducted in partnership with Aboriginal communities.
News & Events
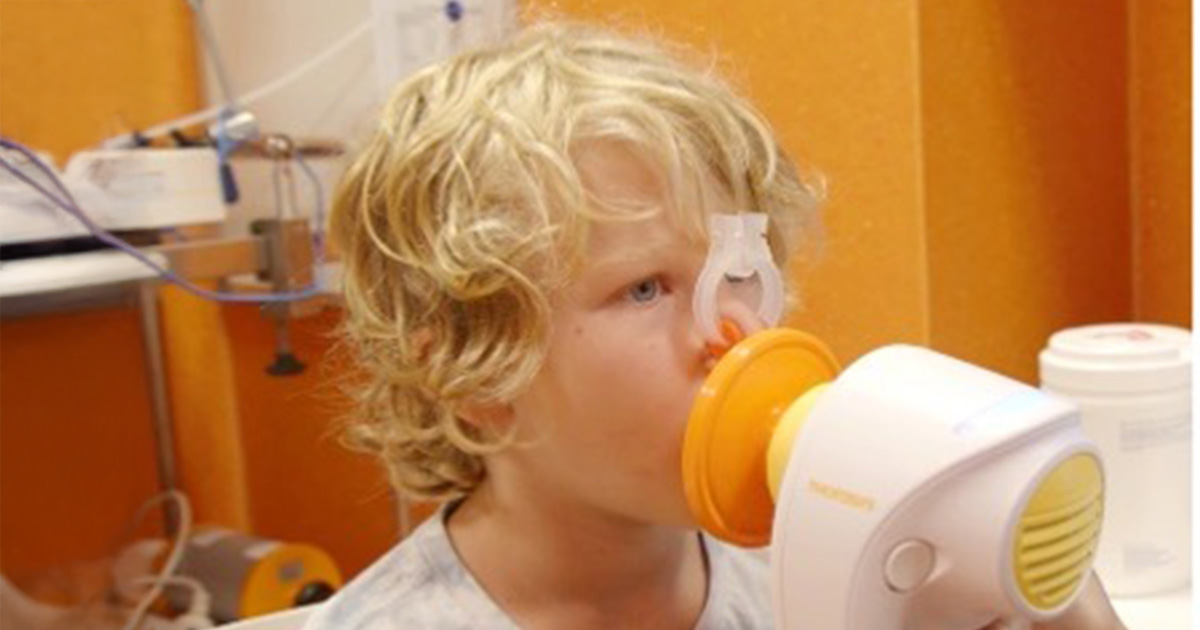
WA researchers lead global centre to eliminate childhood asthmaAn ambitious project that could stop children developing asthma is the centrepiece of a new world-class respiratory research centre launched in Perth.

News & Events
Could Perth lakes hold the secret to fighting antibiotic-resistant superbugs?Perth researchers have discovered a predatory virus living in the city’s lakes and rivers that can fight antibiotic-resistant superbugs in children.
News & Events
WA Cystic Fibrosis Research Collaborative Program GrantsNew hope is on the horizon for people living with cystic fibrosis.
Research
Exploring the Complexity of the Human Respiratory Virome through an In Silico Analysis of Shotgun Metagenomic Data Retrieved from Public RepositoriesRespiratory viruses significantly impact global morbidity and mortality, causing more disease in humans than any other infectious agent. Beyond pathogens, various viruses and bacteria colonize the respiratory tract without causing disease, potentially influencing respiratory diseases’ pathogenesis.
Research
Prematurity-associated lung disease: is it asthma?Shannon Elizabeth Simpson Smith BMedSci (hons), PhD PhD, MSc, BSc Head, Strong Beginnings Research, Co-head Foundations of Lung Disease Program
Research
Neurodevelopmental impairment in children with Robin sequence: A systematic review and meta-analysisEstimate the global prevalence of neurodevelopmental impairment in children with Robin sequence (RS) at one year or more of age.
Research
The longitudinal microbial and metabolic landscape of infant cystic fibrosis: the gut-lung axisIn cystic fibrosis, gastrointestinal dysfunction and lower airway infection occur early and are independently associated with poorer outcomes in childhood. This study aimed to define the relationship between the microbiota at each niche during the first 2 years of life, its association with growth and airway inflammation, and explanatory features in the metabolome.
Research
Azithromycin reduces bronchial wall thickening in infants with cystic fibrosisCOMBAT-CF showed that children aged 0-3 years treated with azithromycin did clinically better than placebo but there was no effect on CT-scores. We reanalysed CTs using an automatic bronchus-artery (BA) analysis.
