Search
News & Events
Call for mental health support for kids with asthmaA new study has found that young children with severe or persistent asthma are at higher risk of developing many common mental health problems.
News & Events
Chance to prevent asthma missedTwo Australian scientists are spearheading an international campaign that's challenging the way asthma drugs are developed and tested.
Research
Blocking Notch3 Signaling Abolishes MUC5AC Production in Airway Epithelial Cells from AsthmaticsWe demonstrate that NOTCH3 is a regulator of MUC5AC production
Research
Whole-cell pertussis vaccine in early infancy for the prevention of allergyThis is a protocol for a Cochrane Review (intervention). The objectives were to assess the efficacy and safety of whole‐cell pertussis (wP) vaccinations in comparison to acellular pertussis (aP) vaccinations in early infancy for the prevention of atopic diseases in children.
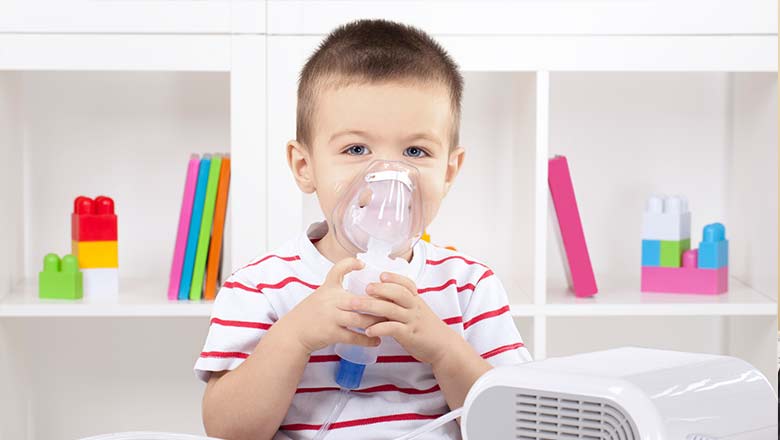

Research
Finding the cellular explanation for recurrent asthma exacerbationsThis study is designed to identify the specific unique immune cell response that occurs in these children with recurrent disease.
Healthy lungs help you to breathe better. This means you can sleep better, as well as play sports, run and walk without being short winded.
News & Events
Very preterm babies at risk of declining lung function throughout childhoodA The Kids Research Institute Australia study published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health has found that survivors of very preterm birth face declining lung function

News & Events
The Kids Research Institute Australia researchers share in TPCHRF fundingEight The Kids Research Institute Australia researchers are among those who have received grant funding from the Telethon-Perth Children’s Hospital Research Fund (TPCHRF).
News & Events
Childhood asthma targeted in new researchNew research aimed at reducing the airway damage caused by asthma attacks in children has just begun at The Kids for Child Health Research in WA.

News & Events
Perth researchers test stress link to asthmaScientists at The Kids for Child Health Research have launched an innovative project to test the relationship between stress and asthma.
