Search

Australian researchers who have conducted the first study looking at the direct health impacts of predicted carbon dioxide levels say the results are worrying and highlight the urgent need for more research into the issue.
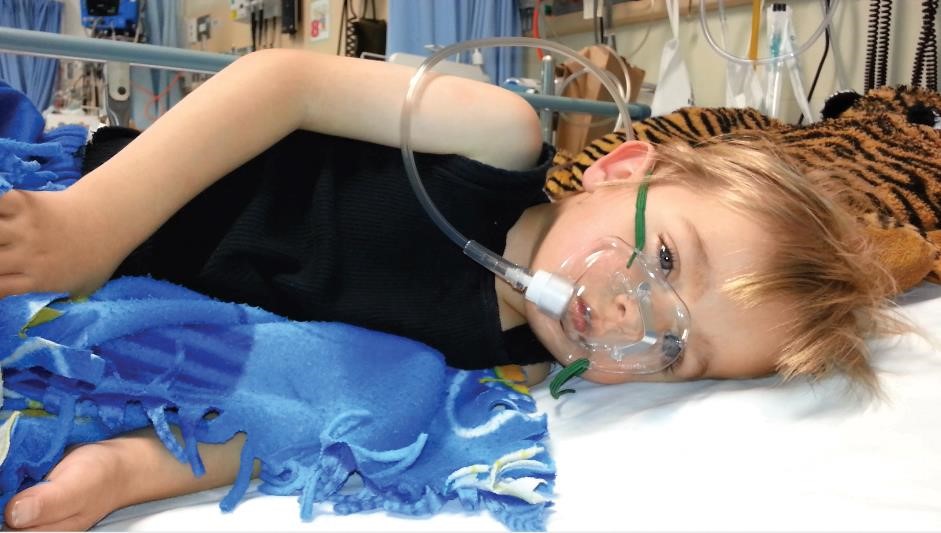
An ambitious project that could stop children developing asthma is the centrepiece of a new world-class respiratory research centre launched in Perth.
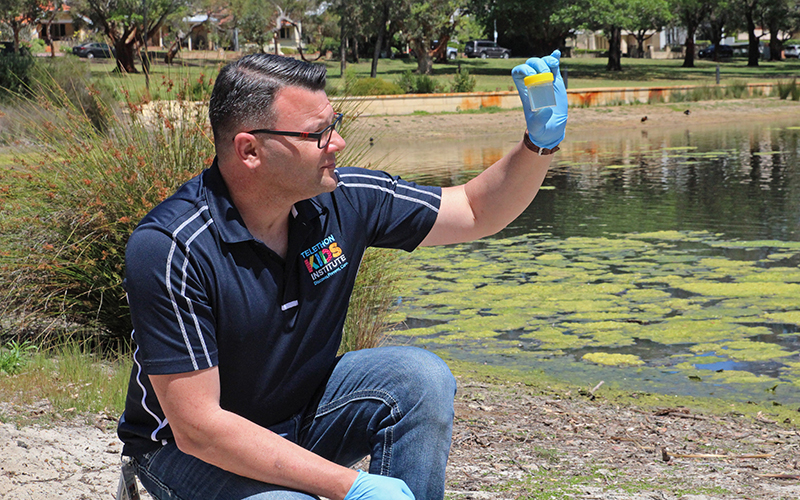

Perth researchers have discovered a predatory virus living in the city’s lakes and rivers that can fight antibiotic-resistant superbugs in children.

Parents of children born prematurely have expressed concerns about their child’s lung health when they exercise, with symptoms such as breathlessness.
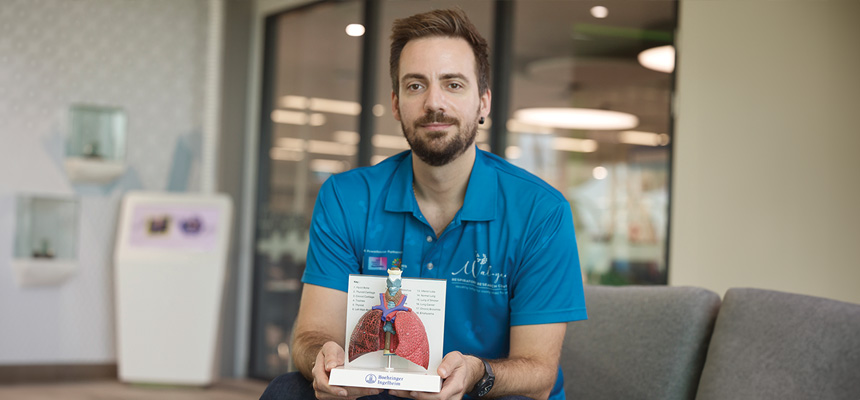

An exciting study is investigating whether a new therapeutic treatment for asthma will protect young sufferers from ongoing lung damage and improve their long-term health outcomes.
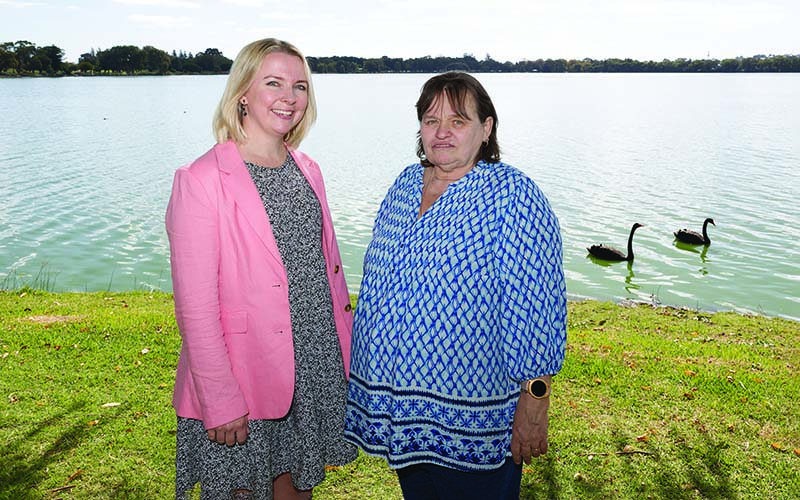

In Aboriginal culture, water is life, holding powerful spiritual and cultural significance and acting as a vital source of connection, food and medicine.

The Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre is a global epicentre for paediatric respiratory research, informing clinical practice and driving a new research agenda for childhood lung health.

The Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre offers a broad range of outpatient and portable tests for those affected by chronic respiratory conditions.

Portable equipment is available to enable bedside and community-led research in rural and remote communities, including Indigenous communities where children are disproportionately affected by chronic respiratory conditions.

One way the Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre provides the opportunity for consumers and community members to contribute to our research is through participation in one of our eight community reference groups.
